6.1 One-factor Redirect Authentication sequence diagram
From CBI GLOBE Wiki
The Redirect Authentication can be used within two different situations:
- Payment transaction, when it is not possible to identify the PSU through the PSU-ID provided by the TPP, independently from the SCA method that will be used by the PSU;
- Consent creation transaction, when it is not possible to identify the PSU through the PSU-ID provided by the TPP and it is necessary to execute a decoupled SCA.
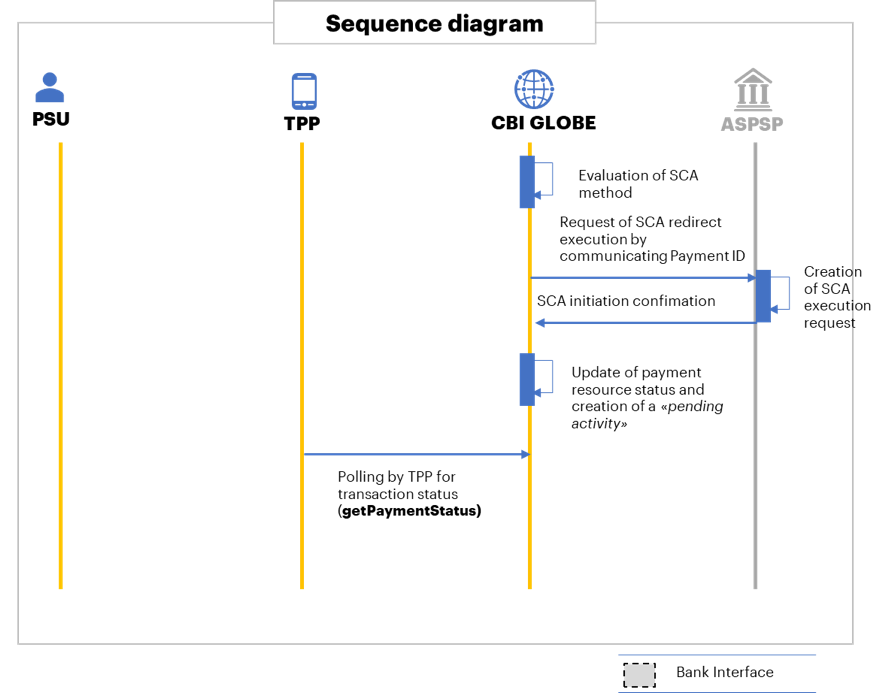
The following steps are the main ones included in the above depicted sequence diagram:
- CBI Globe informs the TPP that it is required the redirect authentication procedure to let the PSU interact with the Bank to be identified. CBI Globe provides the TPP with an authentication URI that is configured in its repository as the redirect authentication URI associated to the ASPSP indicated by the TPP. Details of that URI are described in section 4.3;
- The TPP executes a redirection of PSU application towards the ASPSP, providing the ASPSP with a tppAuthenticationRedirectUri, which is the URI of the TPP where the ASPSP has to redirect the PSU after the authentication;
- The ASPSP redirect authentication web page is displayed to the PSU;
- The PSU enters her/his credentials into the ASPSP web page to be authenticated;
- After PSU authentication the ASPSP executes two different actions:
- It performs a redirection of PSU application towards the TPP, using the tppAuthenticationRedirectUri;
- It invokes proper call-back API to allow CBI Globe to associate a specific PSU-ID to current payment/consent transaction.